tibial torsion test normal range|normal tibial torsion position : supplier torsion tends toward a normal tibial position, with the lateral malleolus 20–30° posterior to the medial malleolus. Virtually all children born with internal tibial torsion have improvement by age 3–5 years. webA cobra faz parte do grupo 9 (nono grupo) do jogo do bicho de um total de 25 bichos que compõem a tabela do jogo do bicho. A cobra representa os números 33, 34, 35 e 36 do jogo do bicho, lembrando que pelas regras do jogo do bicho o grupo é formado pelos últimos dois números do prêmio. Qual bicho jogar quando sonha com cobra?
{plog:ftitle_list}
app Meu Incar? 1. Faça seu download . Clique no botão da lo.
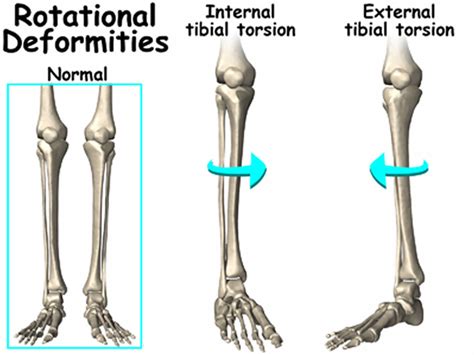
Internal Tibial Torsion is a common condition in children less than age 4 which typically presents with internal rotation of the tibia and an in-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle > 10 degrees of internal rotation in a patient with an in-toeing .External Tibial Torsion is a rare developmental condition in young . External Tibial Torsion is a rare developmental condition in young children caused by abnormal external rotation of the tibia leading to an out-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle measuring greater .Tibial torsion is the twisting of a child’s shinbone, also known as the tibia. In most cases, tibial torsion causes a toddler’s legs and feet to turn inward (internal tibial torsion), giving them a pigeon-toed appearance. Less often, the legs turn .
torsion tends toward a normal tibial position, with the lateral malleolus 20–30° posterior to the medial malleolus. Virtually all children born with internal tibial torsion have improvement by age 3–5 years.
Persistent, excessive torsion can lead to toeing-in and bowlegs. To evaluate for tibial torsion, the angle between the axis of the foot and the axis of the thigh is measured with the child prone . Normal range of external rotation is 45-70°, and internal rotation is 10-45°. As femoral anteversion increases, internal rotation increases and external rotation decreases. .Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. This condition causes a child to have inward-facing toes and bowed legs. It may be caused by the position of the baby in the uterus. A .
External Tibial Torsion. External tibial torsion usually presents between four and seven years of age when the tibia externally rotates during normal growth and worsens into a deformity.
Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically resolves with growth. However, an excessive degree of torsion may indicate a neuromuscular problem. Torsion also occurs with .- normal values: range from about 6-10 deg of external rotation; - thigh foot angle: - measured with the child in the prone position and knee flexed 90 deg, by observing the angle of the foot and the thigh; Foot progression angle can be normal in children with combined torsional deformity (e.g., medial femoral torsion compensated by lateral tibial torsion). 4 Forefoot AlignmentTibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. These bones are located between the knee and the ankle. . walking will become more normal, usually around 5 to 8 years of age. If the case is severe, treatment may help .
Special Test: Tibial Torsion Test PROCEDURE (Seated): tibial torsion is measured by having the patient sit with the knees flexed to 90° over the edge of the examining table. the examiner places the thumb of one hand over the apex of one malleolus and the index finger of the same hand over the apex of the other malleolus. Normally, lateral rotation of the tibia increases from approximately 5º at birth to approximately 15º at maturity; femoral anteversion decreases from approximately 40º at birth to approximately 15º at maturity. Tibial torsion Tibial torsion is inward twisting of the tibia (shinbone) and is the most common cause of intoeing.Tibial torsion can be external (lateral) or internal (medial). (See also Introduction to Congenital Craniofacial and Musculoskeletal Disorders.) External tibial torsion occurs normally with growth: from 0 ° at birth to 20 ° by adulthood. External torsion is rarely a problem. Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically .If the foot points towards the midline this is internal tibial torsion. If the foot points away from the midline this represents external tibial torsion. The normal range is from 10° of internal rotation (-10°) to 15° of external rotation (+15°). We would not consider treatment unless torsion was more than 30°. Picture shows mild external .
- medial tibial torsion is most apparent when infants first begin to walk, . - normal values: range from about 6-10 deg of external rotation; . 5 deg (internal) in infants, but in young children the normal values is about 15 deg; - besides internal tibial .
tibial torsion pictures
tibial torsion normal range
Internal tibial torsion can be diagnosed through a physical exam and measurements of the legs. Internal Tibial Torsion Treatment. This condition usually improves without treatment by about 4 years of age. Bracing, casting and physical therapy are not usually needed. A child’s growth is closely monitored to ensure the internal tibial torsion .
Genu Valgum is a normal physiologic process in children which may also be pathologic if associated with skeletal dysplasia, physeal injury, tumors or rickets. . range 2-8 yrs. Anatomic location. distal femur is the more common location of pathological deformity . . excessive external tibial torsion . idiopathic. post-traumatic . Cozen .
Paediatric lower extremity and gait concerns are common reasons for visits to paediatricians and therapy services.[1][2][3][4][5] They can account for up to 16% of all new paediatric orthopaedic surgeon referrals.[6] Parents commonly worry about in- or out-toeing or that their child might be delayed in meeting developmental milestones because of lower extremity or gait .
Figure 5 provides normal ranges for torsional profile measurements. 8 Measurements outside . Internal tibial torsion is a common normal rotational variant. 3, 19 It is the most common cause of .
Tibial torsion is defined as any twisting of the tibia on its longitudinal axis which produces a change in the alignment of the planes of motion of the proximal and distal articulations ().It undergoes structural remodelling, which begins in utero and progresses throughout childhood and adolescence to skeletal maturity ().The prevalence of rotational pathology of the femur .Tibial Torsion What is tibial torsion in children? Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. . walking will become more normal, usually between ages 5 and 8. If the case is severe, treatment may help straighten the shinbones. Treatment may include: . Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean.Create Personal Test Create Group Test . a simple clinical method of assessing tibial torsion by calculating the transmalleolar axis is presented. The reproducibility of the method is assessed and the transmalleolar axis is computed in 180 normal children and adults. PollTibial torsion is a normal component of growth and development in humans. As we move from quadripedal to bipedal stance, the tibia molds into external torsion and the femur assumes a less anteverted position. . Passive Range of Motion Assessment of the Tibia (Fig. 6.7) . The second-toe test. (A) An external tibial torsion leads to an .
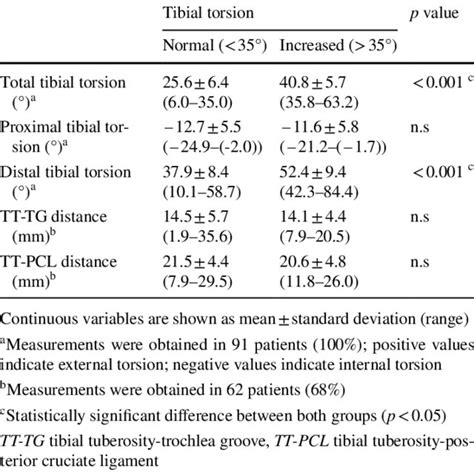
torsion and 3.9° (0.0°–15.0°) for tibial torsion. Mean interreader differences at CT were 3.3° (0.0°–9.0°) for femoral and 3.0° (0.0°–10.0°) for tibial torsion. There was no trend for larger intermethod differences with decreasing age of the children. CONCLUSION. Femoral and tibial torsion measurements in children using 3D models Yoshioka et al 55 determined external torsion of 21° in male patients and 27° in female patients to be normal, more similar to the average 24° originally reported by Le Damany. 52 In a group of 50 normal (asymptomatic) male participants, Seber et al 41 calculated mean external tibial torsion of 30° (range, 16°-50°), whereas CT .
The authors conclude, that clinical measurement of tibial torsion is a reproducible measurement method within an acceptable range. Jakob et al. described in 1981 the measurement of the thigh foot angle in a seating position [ 37 ], whereas Bouchard et al. measured in 2004 the angle between the foot axis and the examination stretcher in patients .Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 1. An inadequately cared for shin contusion may develop into: A. Tibial Torsion B. Tibial Bursitis C. Tibial Periostitis D. Osteomyelitis, 2. The lateral compartment of the leg is comprised of what muscles? A. Tibialis Anterior, Extensor Hallucis Longus, Extensor Digitorum Longus B. Abductor Hallucis, .Mean, standard deviation and range of the values were obtained. Student's t test was used to assess significance of difference between the groups at a P value of 0.05. R ESULTS. . Tibial torsional values from our study should help the surgeon to determine the normal range of tibial torsion to be achieved during TKR, management of complex .
Femoral neck anteversion (FNA) is the angle between the femoral neck and femoral shaft, indicating the degree of torsion of the femur. Differences in FNA affect the biomechanics of the hip, through alterations in factors such as moment arm lengths .Tibial torsion occurs if the child's lower leg (tibia) twists inward. This can occur before birth, as the legs rotate to fit in the confined (limited) space of the womb. After birth, an infant's legs should gradually rotate to align properly. If the lower leg remains turned in, the result is tibial torsion.Tibial Torsion - Etiology, pathophysiology, symptoms, signs, diagnosis & prognosis from the MSD Manuals - Medical Professional Version. . the tibia returns to a normal position without treatment around 5 to 6 years of age. Children who have a severe case of tibial torsion may need to wear orthotics, a cast, or leg braces. Test your Knowledge .
Internal tibial torsion Internal tibial torsion is the most common cause of intoe ‑ ing.14 It is defined by the angular difference between the transmalleolar axis of the ankle and the bicondylar axis of the knee. Clinically, the feet are internally rotated while the patella remains in neutral position (fig 3). Internal tibial torsion is most . Create Group Test Enter Test Code Active Test . residual increased external tibial torsion. limb-length discrepancy. motion. range of motion (ROM) at the hip, knee and ankle should be evaluated. . posterior proximal tibial angle (PPTA) - normal range: 77-84º .
Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. These bones are located between the knee and the ankle. . Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean. . Cedars-Sinai has a range of comprehensive treatment options. See Our Programs Need Help? 1-800-CEDARS-1 (1-800-233-2771) Available 7 days a week, 6 am .
Thereafter only 4° of change occurs until maturity with an average adult external tibial torsion of 38° (range 18–47). Staheli (1993) discovered tibial torsion of 2–4° external at birth, remodeling to 10–20° external at adulthood with a wide range of normal (0–40°). As with femoral anteversion, many neuromuscular or idiopathic .
physical therapy for tibial torsion
normal tibial torsion position
webwebdanfe - Gerador de DANFE em pdf utilizando a API do danfe. About. Módulo node.js para gerar DANFEs em .pdf Resources. Readme License. MIT license Activity. Custom properties. Stars. 50 stars Watchers. 8 watching Forks. 31 forks Report repository Releases 8. Melhoria Latest Apr 28, 2015
tibial torsion test normal range|normal tibial torsion position